Staying cool becomes a primary priority when the sweltering summer heat hits. Although they offer immediate respite, air conditioners can be pricey and energy-intensive. Fortunately, passive cooling offers an alternative that is both economical and environmentally friendly. Finding sustainable and affordable solutions to keep your house and lot for sale cool becomes crucial as the temperatures rise and the desire for comfort increases. Furthermore, to explore the variety of useful and creative strategies for creating a cool air, refreshing living environment without using a lot of air conditioning.
In these upcoming months, the Philippines will experience hot summers. The summer sun and unwanted heat will be mixed in fresh air making it more humid. The air flow will be combined with humidity, hot air, and warm air that will make everyone uncomfortable during the day.
What Is Passive Cooling?
Without significantly depending on mechanical systems like air conditioners, passive cooling is a sustainable and energy-efficient method of cooling down rooms and buildings. It makes use of the laws of physics, ventilation, and clever design to maintain comfortable indoor conditions even in the hottest weather. Passive cooling aims to direct the cooler air into the room without the need for using mechanical systems. It also takes into consideration the idea that warm air rises while cooler air sinks.
The main goal of passive cooling is to reduce heat absorption and increase heat loss from the structure. Passive cooling seeks to achieve a balance between interior and outdoor temperatures by using a number of strategies, guaranteeing a comfortable living or working environment.
Passive cooling lessens dependency on mechanical cooling systems, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. It is a sustainable and affordable alternative. It provides a different strategy that encourages convenience, energy effectiveness, and a healthier indoor environment.

Difference Between Passive and Active Cooling
It’s important to keep in mind that the best thermal comfort and energy efficiency in buildings can be achieved by combining passive and active cooling solutions. The demand for active cooling can be reduced by starting with passive cooling methods, leading to a more hospitable and sustainable inside climate.
- While active cooling depends on active energy consumption, passive cooling minimizes or uses energy consumption passively.
- Since passive cooling methods involve fewer mechanical parts and energy inputs, they are frequently more economical over time.
- Since passive cooling uses less energy and has a smaller carbon impact than active cooling, it is typically thought to be more environmentally friendly.
- Active cooling relies on mechanical systems that need upkeep and regular operation, whereas passive cooling is intended to cooperate with natural elements and building design.
The Benefits And Importance Of Having A Passive Cooling
Passive cooling systems are a desirable alternative to mechanical cooling systems for reducing reliance on them, promoting energy conservation, and creating a comfortable and eco-friendly living or working environment because it offers energy efficiency, cost savings, sustainability, improved indoor comfort, enhanced durability, noise reduction, reliability, and flexibility.
The Different Passive Cooling Techniques
Each passive cooling method focuses on solving a particular component of heat transport and climatic circumstances, different passive cooling methods exist. The goal of passive cooling is to maintain pleasant indoor temperatures by reducing heat intake, enhancing heat dispersion, and utilizing natural features and design solutions. However, depending on variables including the climate, building orientation, architectural style, and regional environmental circumstances, each technique’s efficacy may differ.

As a result, the availability of a variety of ways enables flexibility and adaptation in the implementation of passive cooling solutions depending on the unique needs and limitations of various buildings and locales. Additionally, combining different approaches can have synergistic effects and improve the effectiveness of cooling as a whole.
Natural ventilation, shade, insulation, thermal mass, cool roofing, passive solar design, earth sheltering, and evaporative cooling are examples of passive cooling strategies. In order to lessen the reliance on mechanical cooling systems, increase energy efficiency, improve indoor comfort, minimize heat gain, lower energy costs, lessen environmental impact, increase building durability, provide noise reduction, ensure reliability, and offer flexibility and adaptability to various building types and designs, these techniques make use of natural elements and design principles. You also have to keep in mind the location of where your home is, whether or not the air temperature is hot, as this can affect your techniques on passive cooling.
To list it down, some passive cooling techniques are:
1. Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation utilizes well-placed windows, doors, and vents to enable the flow of cool air and the release of warm air. A simple way to apply this is by opening windows to let in the refreshing cool night air.
2. Thermal Mass
This refers to materials that absorb heat and then release it. Incorporating high thermal mass materials like concrete, brick, or stone in building design allows for heat absorption during the day and gradual release during cooler periods.
3. Evaporative Cooling
Evaporative cooling uses water evaporation to cool the air. By using water-soaked materials or evaporative coolers, heat is absorbed through evaporation, resulting in lower surrounding temperatures.
4. Cross Ventilation
Cross ventilation uses well-positioned windows or vents to enable natural air movement, enhancing cooling by promoting airflow and replacing warm air with cooler air. It improves comfort by facilitating air circulation in a space.
5. Insulation
Properly insulate your home to minimize heat transfer. Materials like foam, fiberglass, or cellulose can be strategically used in walls, roofs, and floors to reduce heat gain.
6. Earth Sheltering
This involves constructing partially or entirely underground structures to harness the insulating properties of the earth.
7. Utilize Shades
Utilize overhangs, awnings, vegetation, or trees, to shield a building from direct sunlight and reduce solar heat gain.
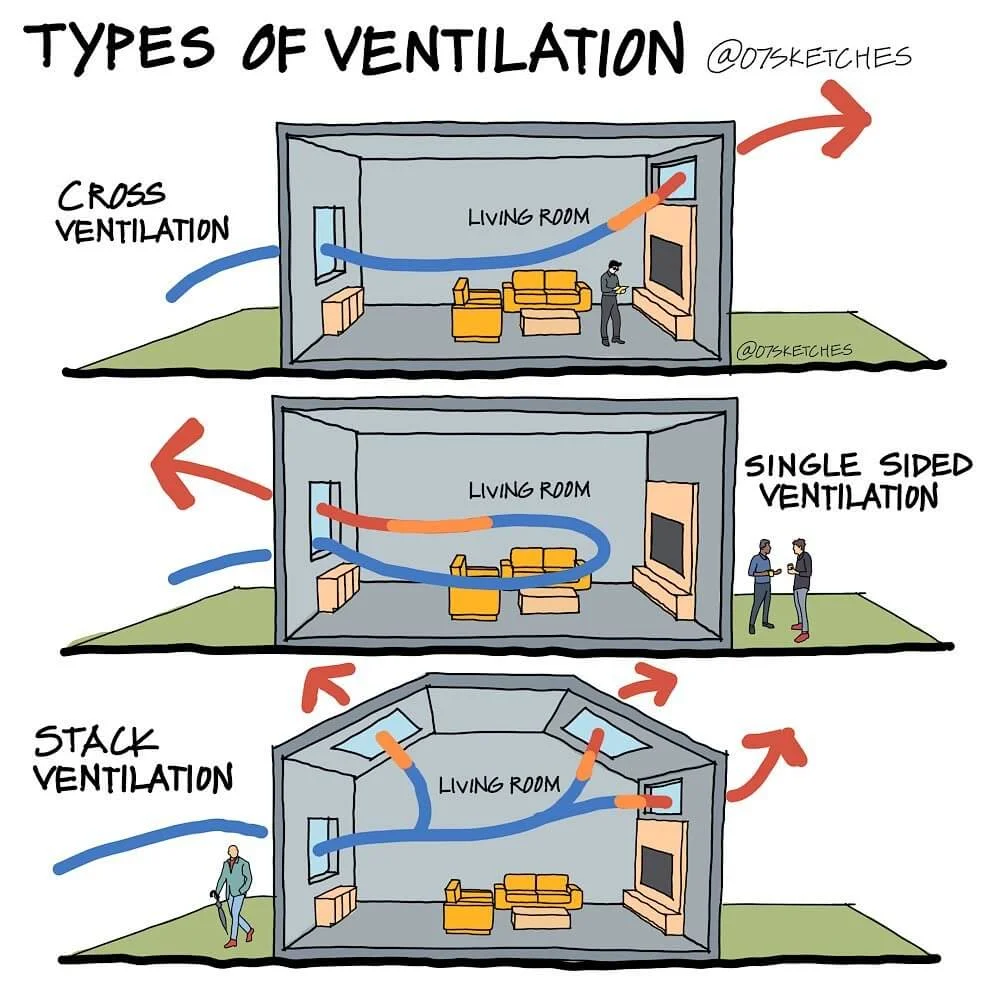
Photo and Idea from 07sketches
How Can People Utilize Passive Cooling Design In Their Houses?
Homeowners can maximize the natural components and characteristics of their homes to produce a more comfortable and energy-efficient living environment by using passive cooling design principles. Here are some ways.
Homeowners can adopt a passive cooling design by orienting their homes with longer sides towards east and west to reduce direct sunlight exposure and heat gain and maintain a cooler internal climate. It is best to strategically put windows on opposing walls to encourage cross-ventilation and natural circulation throughout the entire home. Installation of exterior shade structures, such as overhangs, awnings, or louvers, reduces the need for mechanical cooling by obstructing direct sunlight and preventing heat buildup. Proper wall, roof, and floor insulation prevents heat transfer, maintains a constant inside temperature, and lowers the need for excessive cooling. Utilizing natural ventilation techniques, such as installing roof vents, ridge vents, or moveable windows, allows hot air to exit and cool air to enter.
Moreover, by slowly absorbing and dissipating heat, using materials with high thermal mass in sun-exposed locations helps control indoor temperatures. Using reflecting or light-colored roofing materials keeps the roof and house cooler by reducing heat absorption. Shade-producing plants like trees, shrubs, and vines reduce heat gain and create a cooler microclimate in the landscaping. Low-emissivity coatings or double glazing on energy-efficient windows limit heat gain while decreasing heat transfer and keeping a suitable interior temperature. Finally, planning the layout of the home to guarantee that there are openings on opposite sides of the structure for the natural movement of air.
Is Having Passive Cooling A Good Investment?
Implementing passive cooling strategies may have varying upfront costs based on techniques and project scale. However, the long-term benefits and return on investment make it worthwhile. Factors like local climate, building design, and individual needs should be considered when assessing the investment value. Consulting experts can help evaluate the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of a specific house and lot for sale.
Read more: Cooling your Home this Summer Season


